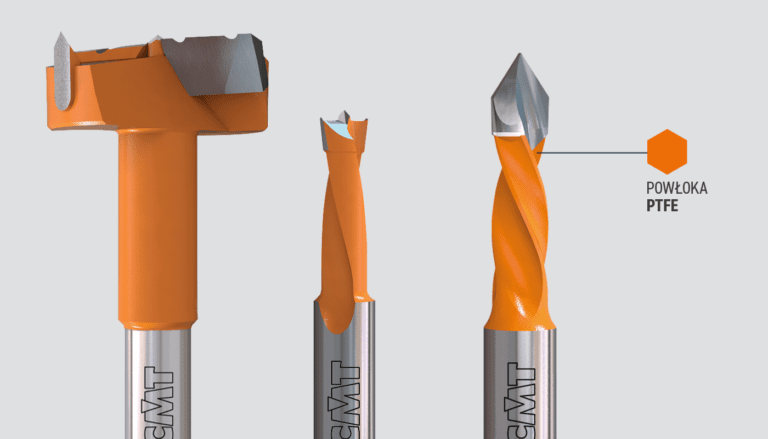
Protective coatings are layers that cover a specific material and are applied to the surface of an object. The coating application can be functional, decorative or both. Functional coatings are usually applied to protect a material or to improve its mechanical, physical or chemical properties. The thickness of a coating is an important parameter that greatly influences its properties. It typically ranges from 1 to 5 microns, or about 1% of the thickness of a human hair.
How are protective coatings applied?
Three main protective coating technologies can be mentioned:
- PE-CVD - is the process of chemical deposition from the gas phase to the solid state on a given substrate, which takes place after the generation of a plasma from reacting gases.
- PVD - is a physical vapour deposition process.
- ARC - pulsed cathodic arc vapourisation method.
In the case of AlTiN and TiSiN coating, cathodic deposition (CathodicARC) is used, in which the application of high current and low voltage to the disc surface creates a cathodic spot at extremely high temperatures (15,000°C), which leads to the vaporisation of the material from the disc. This process is characterised by an extremely high power density, which results in a high level of ionisation by multiply charged ions, neutral particles, clusters and macromolecules.
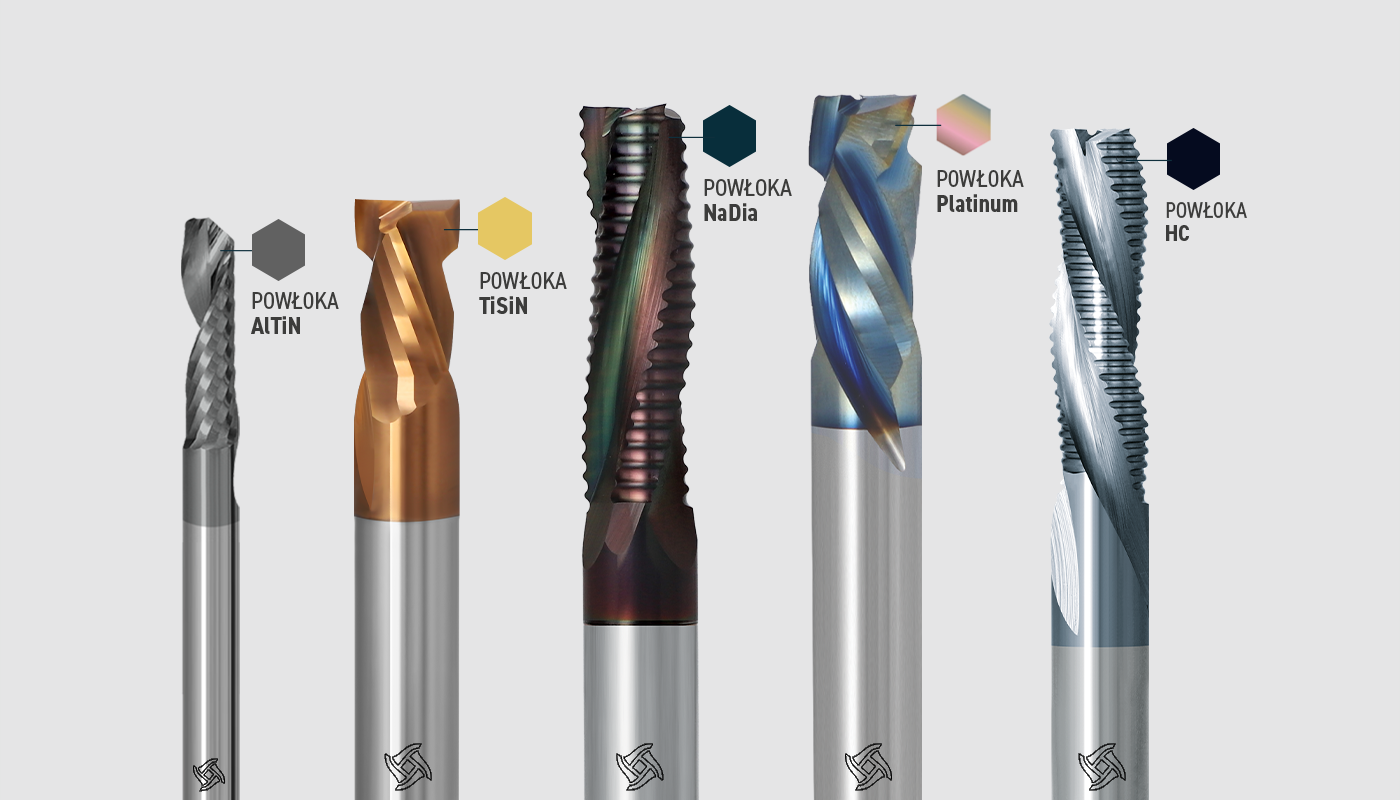
Types of protective coatings
TiSiN
- Copper-coloured,
- Hardness 3570 [HV 0.05],
- Thickness 1-4 [µm].
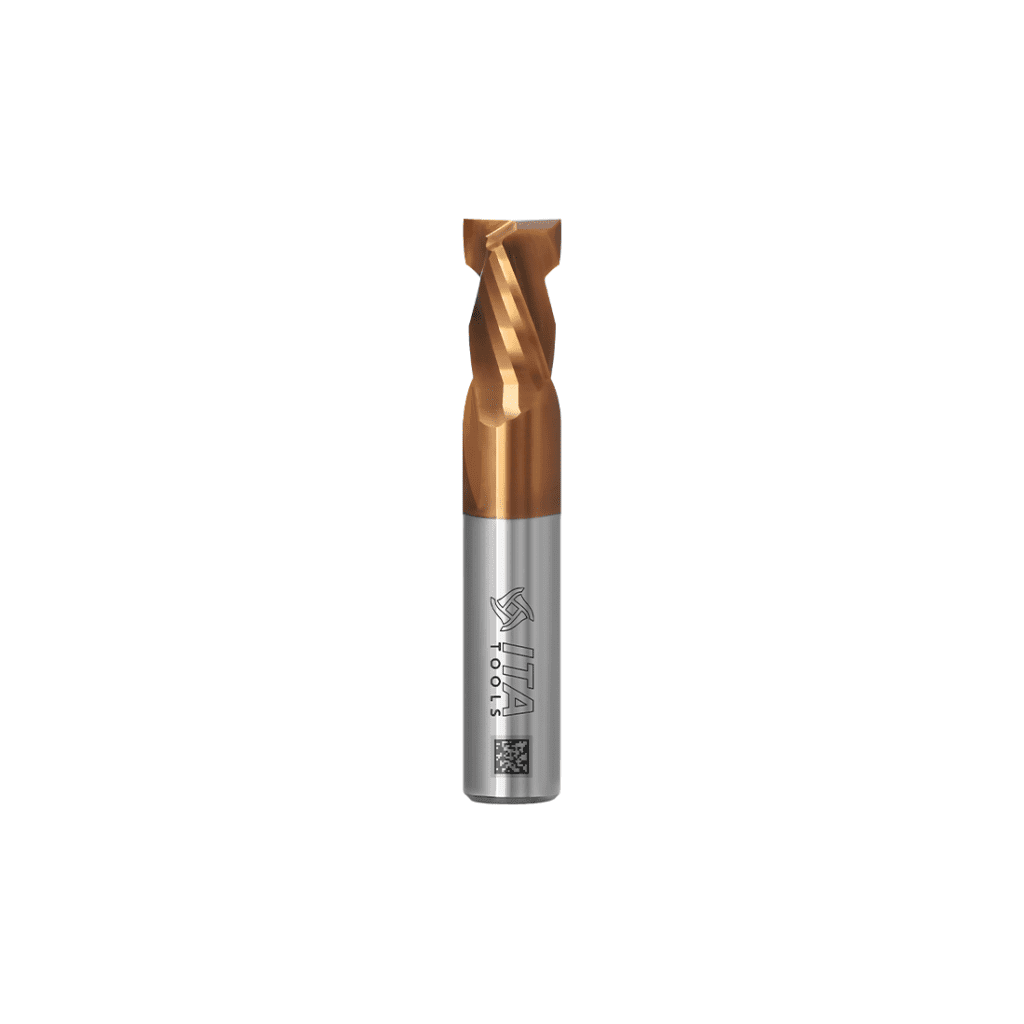


It is characterised by excellent wear resistance even at extreme operating temperatures, for example when machining hard materials. This translates into an extended tool life and significantly reduced need for tool replacement. The cutters last up to 50% longer, guarantee better chip evacuation and reduce heat build-up in the tool.
NaDia
- Colour: black
- Hardness 3650 [HV 0.05],
- Thickness 1-3 [µm].
- Coefficient of friction: 0.01 to 0.05
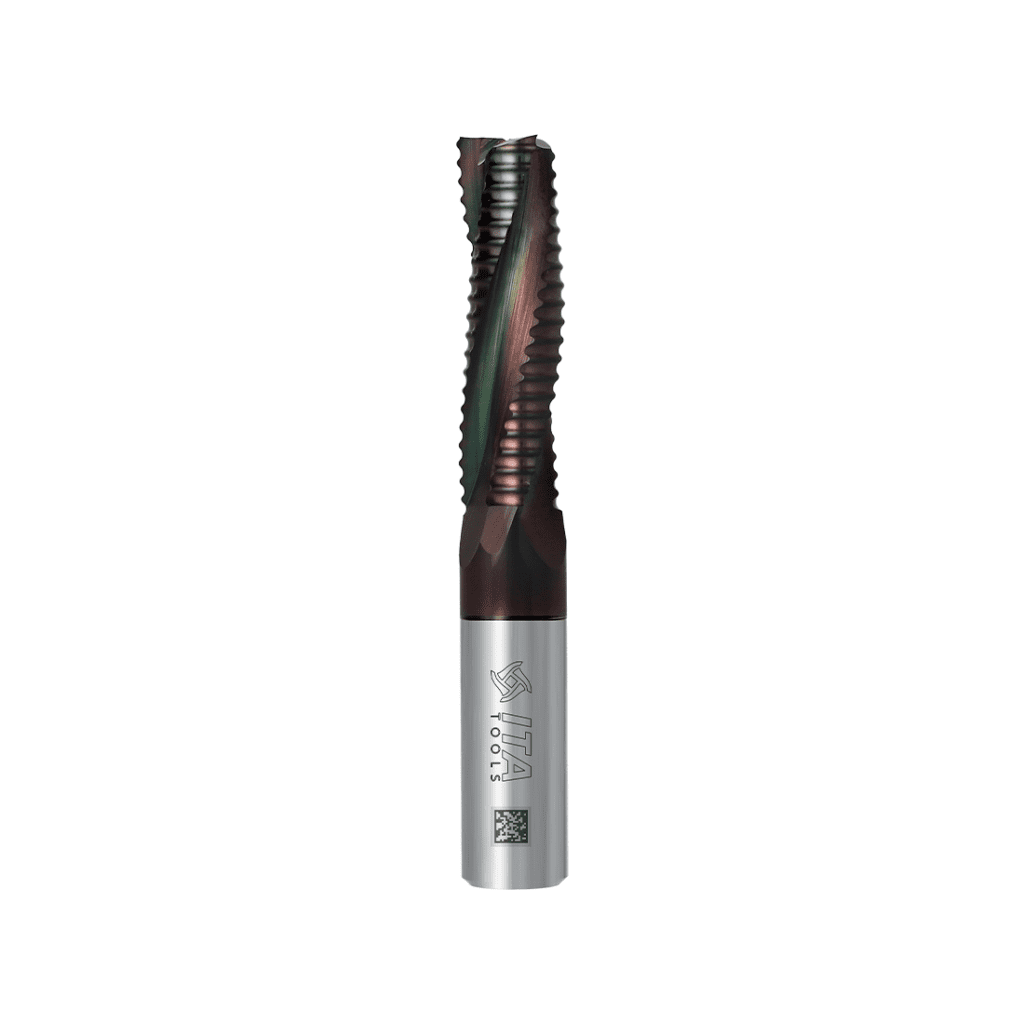


The NaDia coating was developed specifically for the wood sector but given its hardness it is also used in the processing of aluminium and plastics. It is distinguished from the previously discussed coatings by its low coating temperature, high hardness, and low coefficient of friction.
Platinum
- Colour: non-uniform (rainbow)
- Hardness 3500 [HV 0.05],
- Thickness 1-4 [µm].
- Coefficient of friction: 0.2
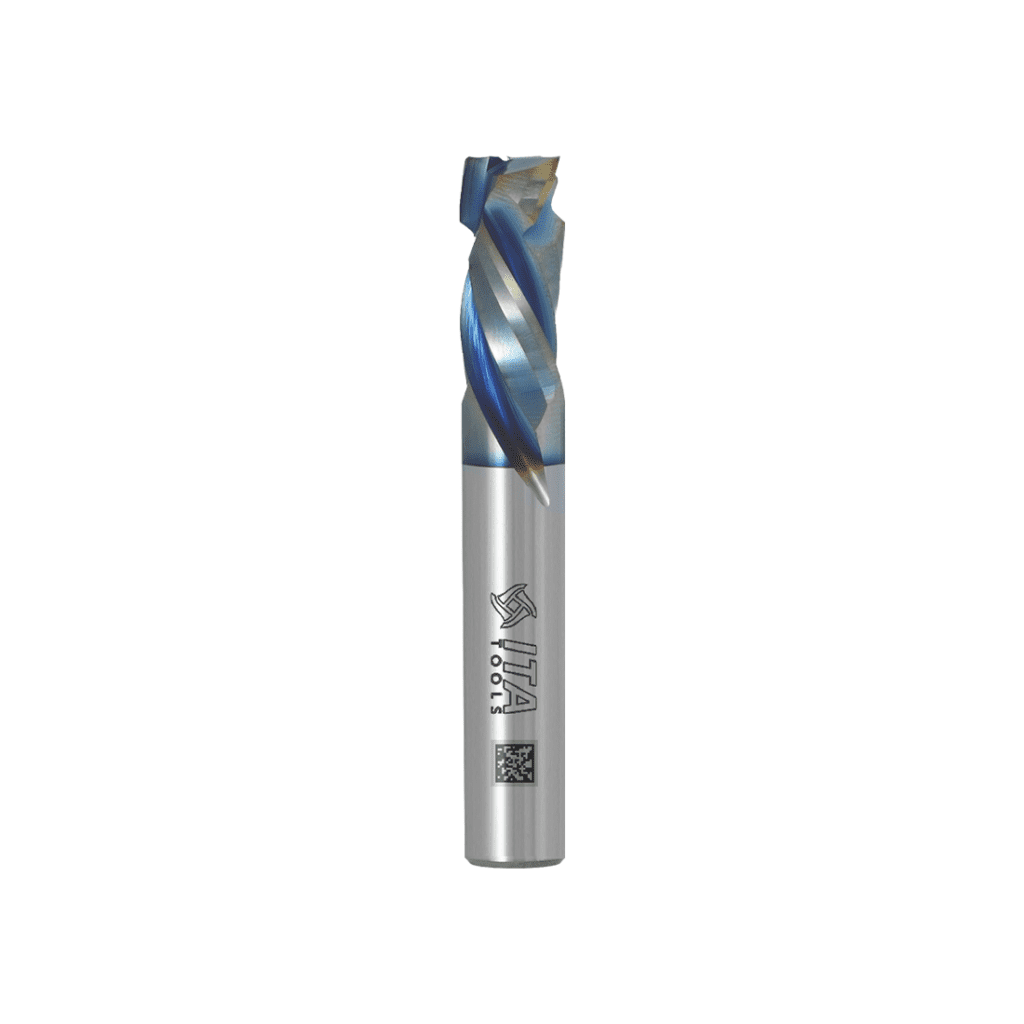


The innovative two-layer PVD coating, which is characterised by its non-uniform colour, is designed for machining hard materials. It optimises the friction coefficient and reduces the adhesion of the workpiece to the surface of the coated tool. The Platinum coating significantly extends tool life and achieves superior workpiece quality.
HC
- Colour: anthracite
- Hardness: 5000-6000 [HV 0.05],
- Thickness 1-2 [µm].
- Coefficient of friction: 0,1-0,2
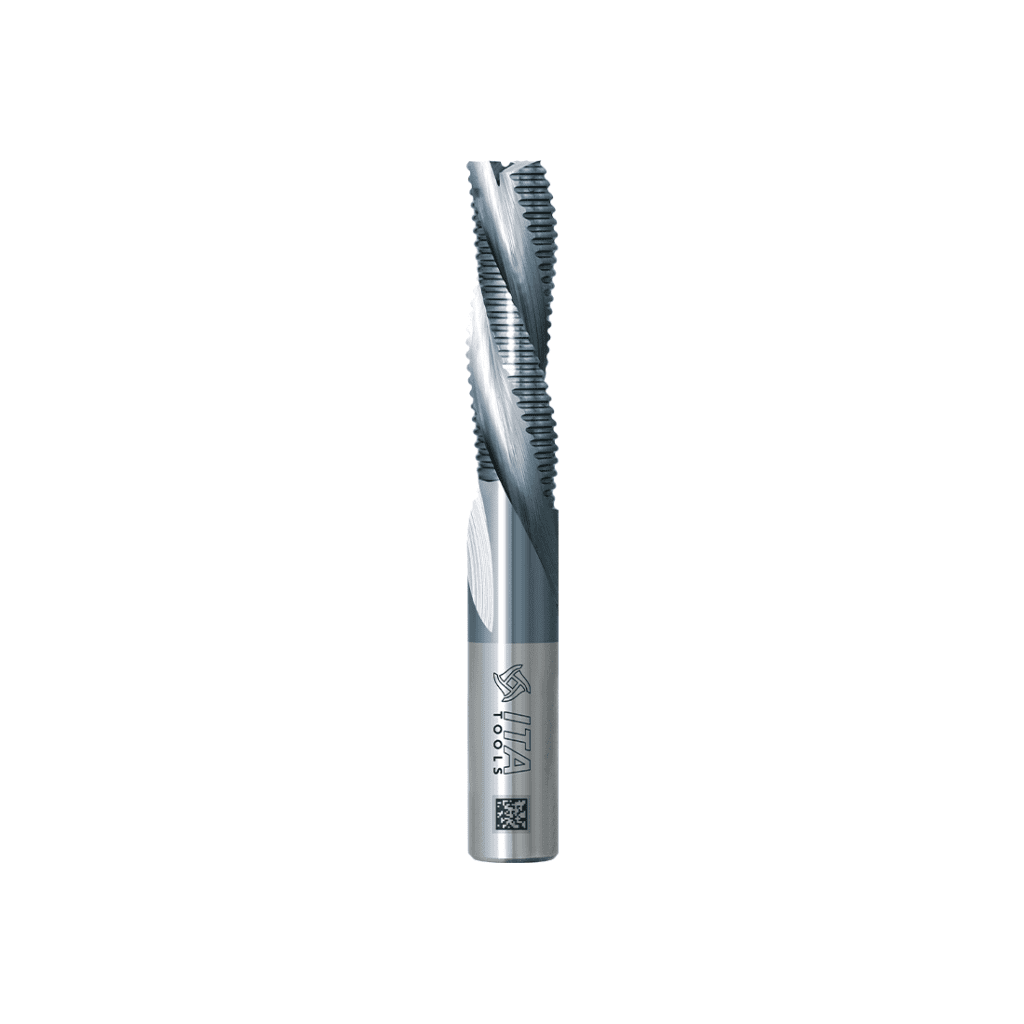


The HC coating is characterised by extremely high hardness, making it dedicated to machining aluminium alloys and composites. An additional advantage is a sharper cutting edge than diamond (PVD) coatings. It is used in the automotive, aerospace and injection moulding industries.
What are the advantages of coatings?
Protective coatings for cutting tools have a number of advantages that have a positive impact on the operation of the tool and the final quality of the machined materials. The main advantages of coatings are:
- greater tool wear resistance,
- reduced coefficient of friction,
- increased corrosion resistance,
- slower tool wear, which translates into longer tool life,
- reduced adhesion of the workpiece to the surface,
- increase in operating parameters (feed and speed) relative to each other for uncoated tools,
- increased productivity thanks to shorter downtimes.
Thanks to our many years of experience in the industry and our wide range of products, we are able to tailor tools perfectly to our customers' needs. Contact us today.